Introduction
In the world of computer peripherals, a plotter is a crucial hard copy output device used for producing high-precision graphical outputs. Unlike traditional printers, plotters use pen-based mechanisms to draw continuous lines, making them ideal for engineering, architectural, and design applications.

In this blog, we will explore:
What is a Plotter?
Types of Plotters
Features of Plotters
Applications & Advantages
Comparison of Plotters vs. Printers
What is a Plotter?
A plotter is an output device that generates vector graphics. Unlike traditional printers that use dots to form images, plotters create continuous, high-precision drawings using pens or blades. They are widely used in CAD (Computer-Aided Design), architectural drawings, and industrial designs.
✔ Uses: Engineering designs, architectural blueprints, business graphics, advertising banners, sign-making, and 3D modeling.
✔ Industries: Architecture, Engineering, Graphic Design, Manufacturing, and Medical Fields
.
Types of Plotters
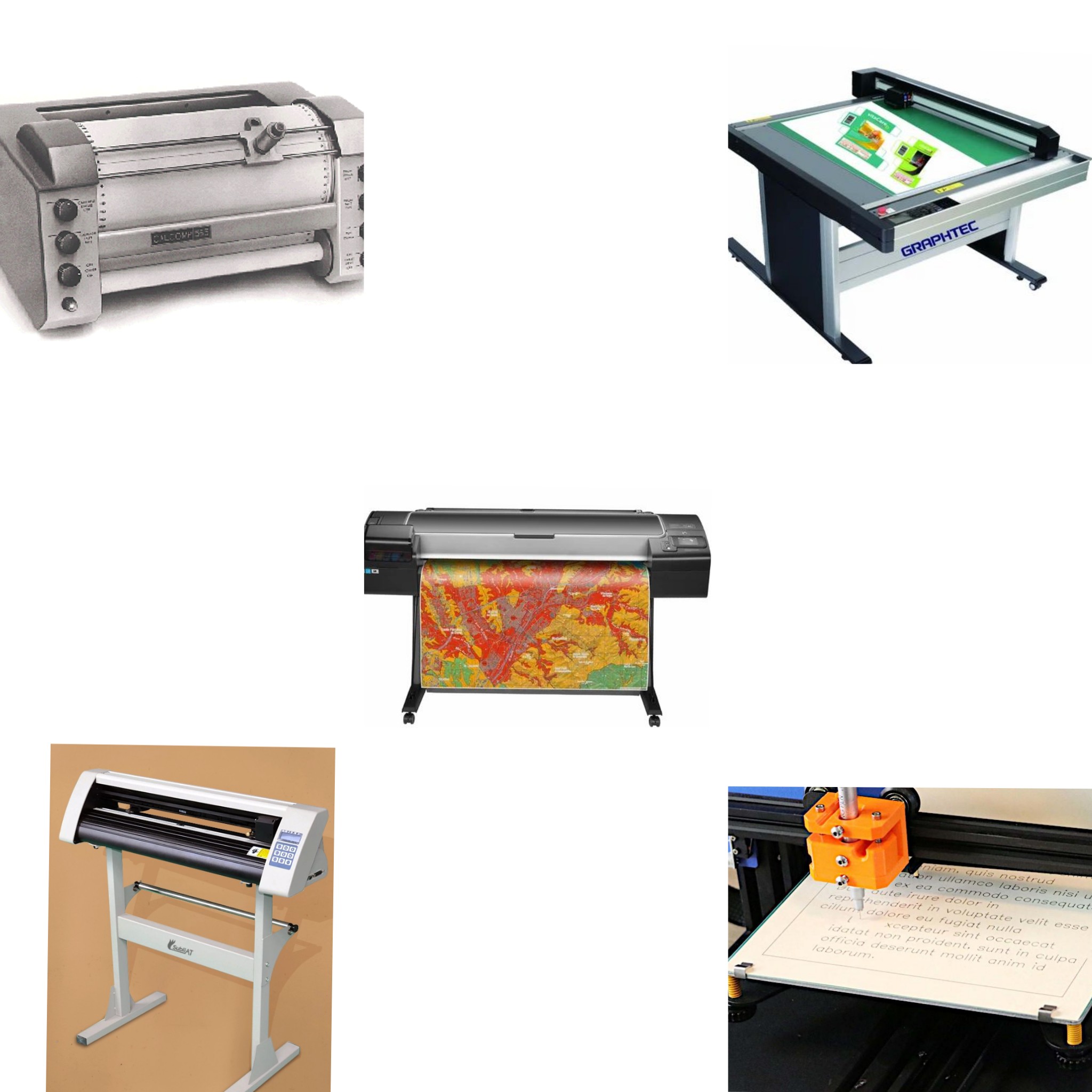
1. Drum Plotter
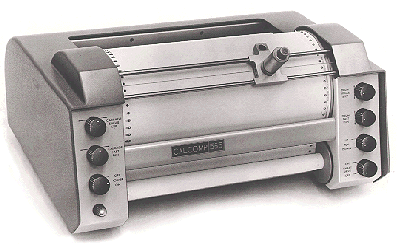
Uses a rotating drum where paper moves while the pen draws.
Suitable for large-scale technical drawings.
✅ Uses: Blueprints, circuit designs, and large-scale technical drawings.
✅ Industries: Architecture, engineering, and GIS mapping.
✅ Advantages: Can print long documents without page breaks.
2. Flatbed Plotter

Paper remains stationary while the pen moves over it.
Used for high-precision blueprints and design prints.
✅ Uses: Technical schematics, artistic designs, and scientific drawings.
✅ Industries: Manufacturing, research, and creative design fields.
✅ Advantages: Highly precise, can print on multiple surfaces.
3. Inkjet Plotter

Functions like an inkjet printer but designed for larger formats.
Used for posters, banners, and commercial printing.
✅ Uses: Advertising, posters, maps, and high-quality graphics.
✅ Industries: Marketing, publishing, and graphic design.
✅ Advantages: Full-color printing, fast and cost-effective.
4. Cutting Plotter
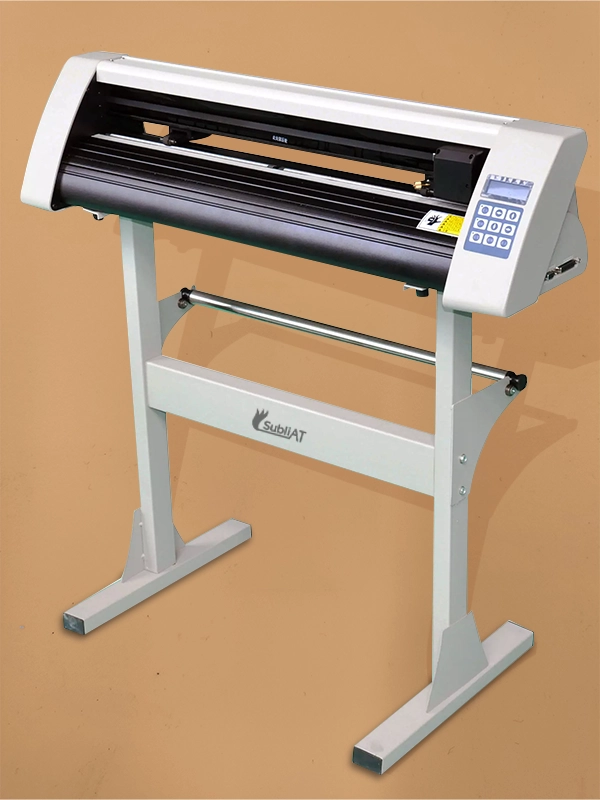

Uses a blade instead of a pen to cut designs on vinyl or fabric.
Popular in sticker printing, sign-making, and textile industries.
✅ Uses: Stickers, signage, decals, labels, and branding materials.
✅ Industries: Advertising, vehicle wrapping, and promotional products.
✅ Advantages: Can cut complex designs with precision.
5. 3D Plotter
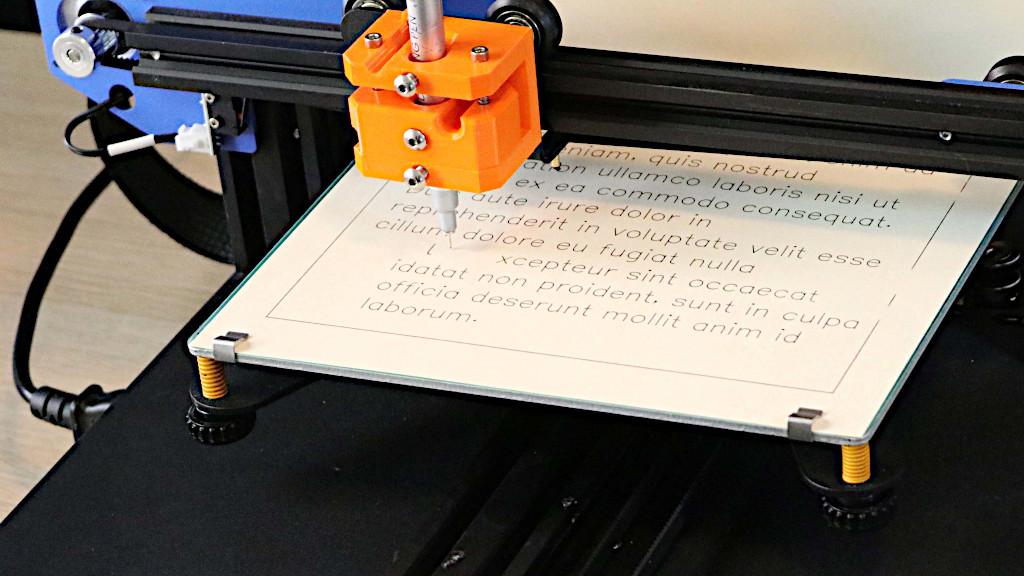
Advanced plotters capable of creating 3D models.
Used in prototyping,
architecture, and product design.
✅ Uses: Prototyping, modeling, and custom 3D object creation.
✅ Industries: Automotive, medical, aerospace, and education.
✅ Advantages: Creates realistic 3D models quickly.
Features of Plotters
High Precision: Ideal for detailed engineering and architectural work.
Large Format Printing: Can print on bigger paper sizes than standard printers.
Vector Graphics Support: Uses continuous lines instead of dots.
Multiple Color Options: Supports monochrome & multicolor outputs.
Durability: Designed for heavy-duty industrial use.
Applications of Plotters
Engineering & CAD Drawings – Used in blueprints and schematics.
Architectural Designs – For building plans and 3D layouts.
Textile & Fashion Industry – Helps in pattern-making and fabric cutting.
Advertising & Signage – Used for banners, posters, and vinyl stickers.
Medical Imaging – Produces detailed diagrams for research and diagnostics
Plotters vs. Printers – Key Differences
| Feature | plotter | printer |
| Output type | vector graphics | Raster graphics |
| Precision | High | moderate |
| Use case | technical drawings | text & images |
| Paper size | Large format | standard sizes |
| Speed | slower (but more accurate) | faster |
Advantages of Using a Plotter
✅ Perfect for professionals requiring high-detail output.
✅ Supports large-scale designs without compromising quality.
✅ Essential in industries like CAD, engineering, and fashion.
✅ Durable and reliable for long-term industrial use.
Conclusion
Plotters play a crucial role in technical, industrial, and commercial fields, offering precision and high-quality output. From architectural blueprints to textile designs, plotters remain an essential tool for professionals and students alike.

Leave a Reply