1. Phylum Protozoa:
General Characteristics:ये single-celled, eukaryotic organisms होते हैं, जो microscopic होते हैं और aquatic या moist environments में पाए जाते हैं।
Protozoa में locomotion के लिए तीन structures होते हैं: cilia (छोटे बाल जैसे projections), flagella (लंबी whip-like structure), या pseudopodia (false feet जैसी structure)।
Nutrition के प्रकार के आधार पर ये holozoic (solid particles खाते हैं), saprozoic (dissolved substances absorb करते हैं), या parasitic (दूसरे organisms पर निर्भर होते हैं) हो सकते हैं।इनका reproduction ज्यादातर asexual होता है, जो binary fission के through होता है। कुछ cases में sexual reproduction भी देखा जाता है, जैसे conjugation के माध्यम से।
Classification up to Orders:
Protozoa को चार प्रमुख classes में बांटा गया है:
1. Rhizopoda (Sarcodina): इनका locomotion pseudopodia से होता है। उदाहरण: Amoeba।
2. Ciliophora: ये cilia का उपयोग करते हैं movement के लिए। उदाहरण: Paramoecium।
3. Flagellata (Mastigophora): ये flagella से move करते हैं। उदाहरण: Euglena।
4. Sporozoa: इनमें कोई locomotory organelle नहीं होती है और ये mostly parasitic होते हैं। उदाहरण: Plasmodium (जिससे malaria होता है)।
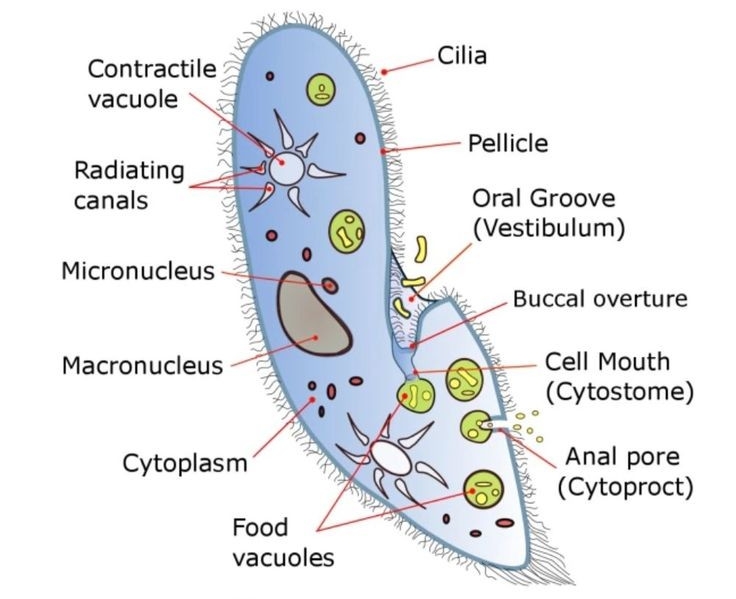
Type Study – Paramoecium:
Paramoecium एक slipper-shaped, ciliated protozoan है जो freshwater में पाया जाता है।
इसमें दो types के nucleus होते हैं: macronucleus (जिससे metabolic functions control होते हैं) और micronucleus (जो reproduction में मदद करता है)।Locomotion और feeding के लिए cilia का उपयोग किया जाता है।
2. Phylum Porifera:
ये simplest multicellular animals हैं, जिनका body structure porous होता है (जिससे पानी अंदर और बाहर जाता है)।इनका body canal system से बना होता है, जिसमें pores, canals, और chambers होते हैं, जो filter feeding के लिए उपयोग होते हैं।
Porifera mostly marine होते हैं और इनमें कोई definite symmetry या tissues नहीं होते।इनका skeleton spicules या spongin fibers से बना होता है, जो body को support देते हैं।
Reproduction asexual (budding और fragmentation) और sexual दोनों तरीकों से होता है।
Classification up to Orders:
Porifera को तीन classes में बांटा गया है:
1. Calcarea: इनके spicules calcium carbonate के बने होते हैं। उदाहरण: Sycon।
2. Hexactinellida: इनके spicules silica के बने होते हैं और ये mostly deep sea में पाए जाते हैं। उदाहरण: Euplectella।
3. Demospongiae: इनका skeleton spongin fibers और silica spicules से बना होता है। उदाहरण: Spongilla।
Type Study – Sycon:
Sycon एक small, tubular sponge है जो marine environments में पाया जाता है।
इसका body structure simple canal system के साथ होता है, जिसमें pores से पानी अंदर आता है और osculum से बाहर निकलता है।Sycon filter feeder होता है और पानी से छोटे organic particles को filter करता है।
3. Phylum Coelenterata (Cnidaria):
General Characteristics:
ये aquatic, mostly marine organisms होते हैं, जिनका body radial symmetry के साथ होता है।इनका body दो layers से बना होता है: epidermis (outer layer) और gastrodermis (inner layer), जो mesoglea से अलग होते हैं।
इनका digestive cavity केवल एक opening (mouth) के साथ होता है।Defense और prey capture के लिए इनके पास stinging cells (cnidocytes) होते हैं
।इनका reproduction दोनों तरीकों से हो सकता है: asexual (budding) और sexual (gametes का production)।
Classification up to Orders:
Coelenterata को चार classes में बांटा गया है:
1. Hydrozoa: इनमें polyp और medusa दोनों forms होते हैं। उदाहरण: Hydra, Obelia।
2. Scyphozoa: इनमें medusa dominant form होती है। उदाहरण: Aurelia (jellyfish)।
3. Cubozoa: इनमें box-shaped medusa होती है। उदाहरण: Chironex।
4. Anthozoa: इनमें केवल polyp form होती है और ये sessile होते हैं। उदाहरण: Sea anemones, Corals।
Type Study – Obelia:
Obelia एक colonial coelenterate है जो marine environments में पाया जाता है।
इसका life cycle alternation of generations दिखाता है, जिसमें polyp (asexual) और medusa (sexual) forms alternate होते हैं।
Obelia के tentacles पर cnidocytes होते हैं, जो prey को पकड़ने और सुरक्षा के लिए उपयोग होते हैं।

Leave a Reply