In today’s digital world, the Central Processing Unit (CPU) plays a pivotal role in ensuring seamless computing experiences. Whether you’re a student learning about computer basics or diving deeper into computer science, understanding the CPU and its components is essential. This guide provides an easy-to-follow explanation to help students worldwide, especially in India, grasp this crucial topic.
What Is a CPU?
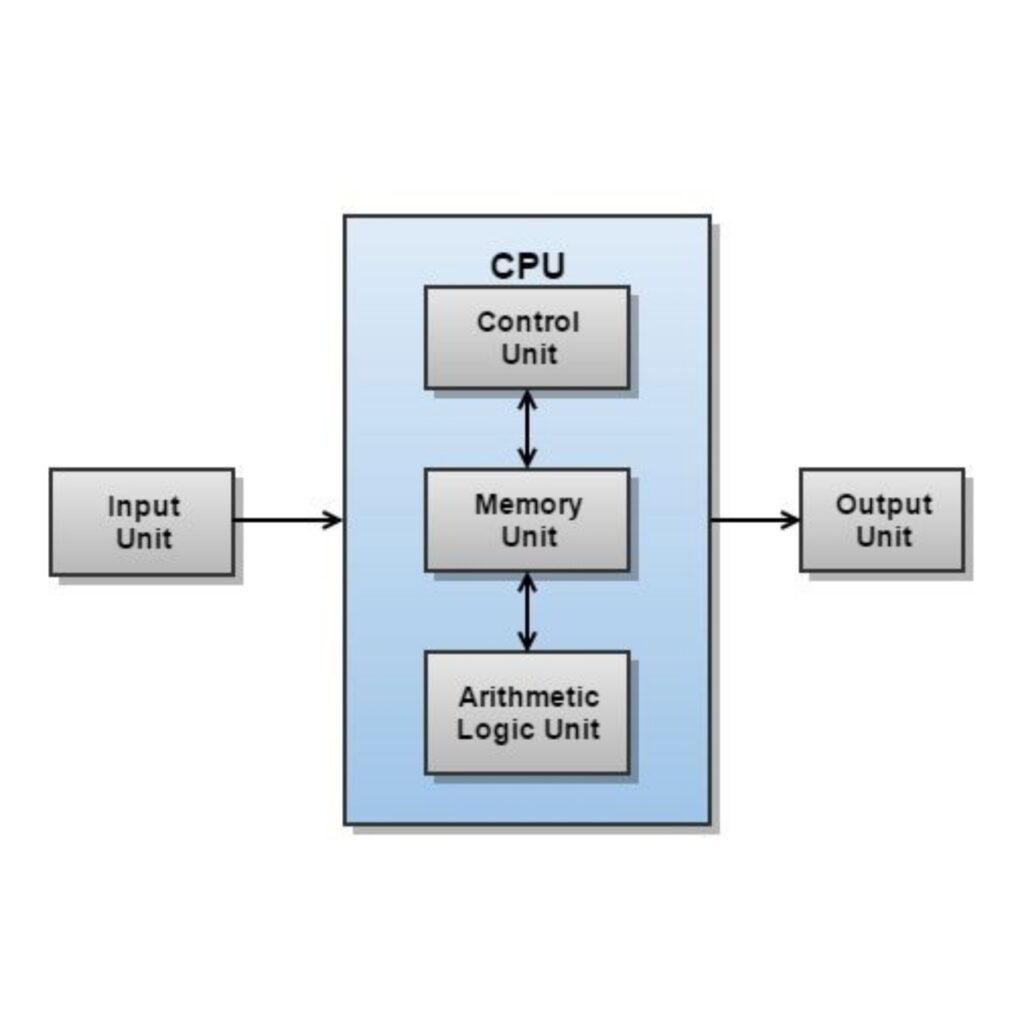
The CPU, often referred to as the “brain” of the computer, is responsible for executing instructions and performing calculations. It processes data and controls the operation of other hardware components, enabling your computer to function efficiently. Without a CPU, no digital device—from smartphones to supercomputers—could operate.

Key Functions of a CPU
Processing Data: Executes instructions from software applications.
Controlling Operations: Manages and coordinates the activities of all computer components.
Storing Temporary Data: Temporarily stores information in its registers for quick access.
Performing Arithmetic and Logical Operations: Handles mathematical calculations and logical comparisons.
Main Components of a CPU
To understand the CPU better, let’s explore its three primary components:
1. Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
The ALU is the part of the CPU that handles arithmetic and logical operations. It performs tasks like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and logical comparisons (e.g., greater than, less than). Every calculation or decision the computer makes is processed here.
2. Control Unit (CU)
The Control Unit acts as the CPU’s manager. It directs the flow of data and instructions between the CPU and other hardware. The CU interprets instructions from programs and tells the ALU, memory, and input/output devices what to do. Essentially, it coordinates all activities within the CPU.
3. Registers
Registers are small, high-speed storage areas within the CPU. They temporarily hold data, instructions, and addresses being processed. Types of registers include:
Instruction Register (IR): Holds the current instruction.
Program Counter (PC): Keeps track of the next instruction.
Accumulator (AC): Stores intermediate results of calculations.
How the CPU Works
The CPU operates in cycles, commonly known as the Fetch-Decode-Execute Cycle:
1. Fetch: The Control Unit retrieves instructions from the computer’s memory.
2. Decode: The CPU decodes these instructions to determine the required action.
3. Execute: The ALU performs the necessary calculations or logical operations.
This cycle repeats millions of times per second, enabling your computer to execute tasks rapidly.
Types of CPUs
1. Single-Core CPU
The earliest type of CPU, which can execute one task at a time. It is now obsolete due to its slower performance.
2. Dual-Core and Multi-Core CPUs
Modern CPUs often have multiple cores, allowing them to handle multiple tasks simultaneously. For instance, quad-core CPUs have four cores, making them efficient for multitasking.
3. Specialized CPUs
GPUs (Graphics Processing Units):
Designed for rendering images and handling graphics-related tasks.
APUs (Accelerated Processing Units):
Combine a CPU and GPU on a single chip.
Factors Affecting CPU Performance
Several factors influence how efficiently a CPU performs:
Clock Speed: Measured in GHz, it determines how many instructions the CPU can execute per second. A higher clock speed generally means faster performance.
Cache Memory: Temporary storage for frequently accessed data, reducing the time taken to fetch information from main memory.
Number of Cores: More cores mean the CPU can handle more tasks simultaneously.
Instruction Set: A set of commands the CPU understands. Modern CPUs use advanced instruction sets like x86-64 for better performance.
Popular CPU Manufacturers
The two leading CPU manufacturers globally are:
Intel: Known for its Core i3, i5, i7, and i9 processors.
AMD (Advanced Micro Devices): Famous for its Ryzen series, which provides excellent value for money.
Both companies continue to innovate, offering CPUs tailored to different needs, from budget-friendly options to high-performance models.
Applications of CPUs
CPUs are integral to almost every device, powering:
Personal Computers (PCs): For tasks like browsing, gaming, and office work.
Smartphones: Enabling apps, communication, and media playback.
Servers: Handling massive amounts of data in data centers.
Embedded Systems: Found in devices like washing machines and smart TVs.
Future of CPUs
As technology evolves, CPUs are becoming faster and more efficient. Innovations like quantum computing and AI-driven processing are pushing the boundaries of what CPUs can achieve. For students, staying updated with these advancements is essential to understanding the future of technology.
Key Takeaways
The CPU is the core of any computing device, responsible for executing instructions and managing hardware.
Its main components include the ALU, Control Unit, and Registers.
Factors like clock speed, cache memory, and the number of cores affect CPU performance.
Leading manufacturers like Intel and AMD continue to shape the CPU landscape with cutting-edge innovations.
Conclusion
Understanding the CPU and its components is vital for anyone studying computer science or using digital devices. This knowledge not only helps in academics but also lays the foundation for a deeper appreciation of how technology works. Whether you’re in India or anywhere in the world, mastering this topic equips you with insights into one of the most critical aspects of modern computing.

Leave a Reply